Publications
Publications by categories in reversed chronological order. For more details, please check my Google Scholar.
2025
- arXiv
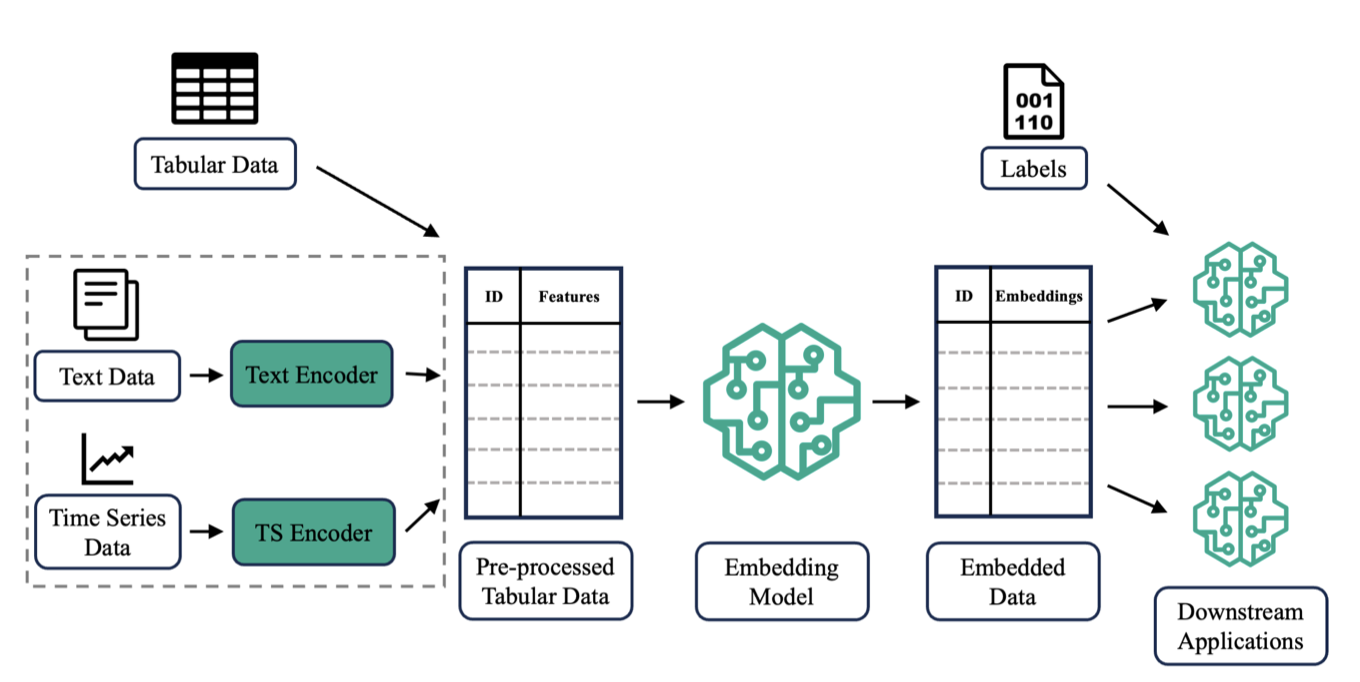 Autoencoder-based General Purpose Representation Learning for Customer EmbeddingJan Henrik Bertrand, David B. Hoffmann, Jacopo Pio Gargano, and 2 more authorsFeb 2025
Autoencoder-based General Purpose Representation Learning for Customer EmbeddingJan Henrik Bertrand, David B. Hoffmann, Jacopo Pio Gargano, and 2 more authorsFeb 2025Recent advances in representation learning have successfully leveraged the underlying domain-specific structure of data across various fields. However, representing diverse and complex entities stored in tabular format within a latent space remains challenging. In this paper, we introduce DEEPCAE, a novel method for calculating the regularization term for multi-layer contractive autoencoders (CAEs). Additionally, we formalize a general-purpose entity embedding framework and use it to empirically show that DEEPCAE outperforms all other tested autoencoder variants in both reconstruction performance and downstream prediction performance. Notably, when compared to a stacked CAE across 13 datasets, DEEPCAE achieves a 34% improvement in reconstruction error.
@misc{bertrand2025_deepcae, title = {Autoencoder-based General Purpose Representation Learning for Customer Embedding}, author = {Bertrand, Jan Henrik and Hoffmann, David B. and Gargano, Jacopo Pio and Mombaerts, Laurent and Taws, Jonathan}, year = {2025}, month = feb, day = {28}, eprint = {2402.18164}, archiveprefix = {arXiv}, primaryclass = {cs.LG}, url = {https://arxiv.org/abs/2402.18164}, }
2024
- arXiv
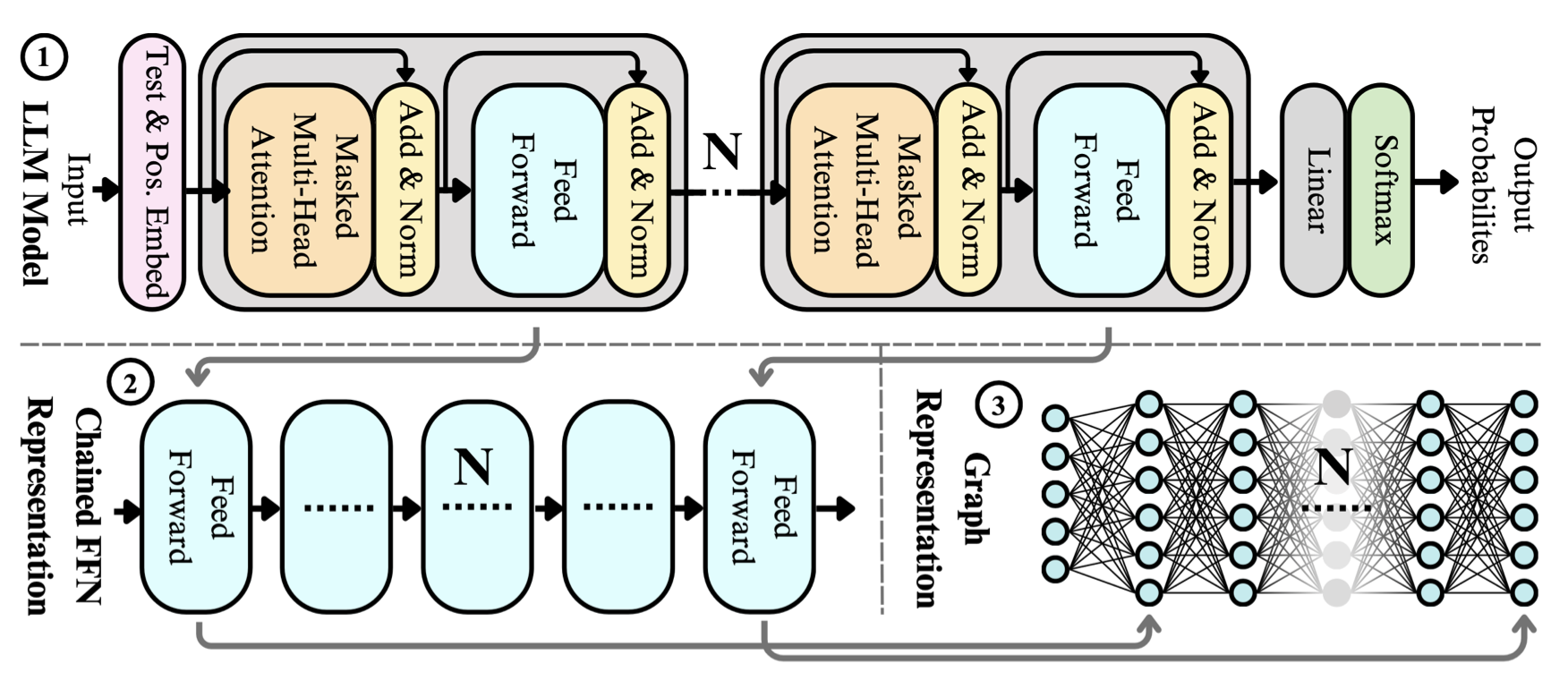 LLM-Rank: A Graph Theoretical Approach to Pruning Large Language ModelsDavid B. Hoffmann, Kailash Budhathoki, and Matthaeus KleindessnerOct 2024
LLM-Rank: A Graph Theoretical Approach to Pruning Large Language ModelsDavid B. Hoffmann, Kailash Budhathoki, and Matthaeus KleindessnerOct 2024The evolving capabilities of large language models are accompanied by growing sizes and deployment costs, necessitating effective inference optimisation techniques. We propose a novel pruning method utilising centrality measures from graph theory, reducing both the computational requirements and the memory footprint of these models. Specifically, we devise a method for creating a weighted directed acyclical graph representation of multilayer perceptrons to which we apply a modified version of the weighted PageRank centrality measure to compute node importance scores. In combination with uniform pruning this leads to structured sparsity. We call this pruning method MLPRank. Furthermore we introduce an extension to decoder-only transformer models and call it LLMRank. For both variants we demonstrate a strong performance. With MLPRank on average leading to 6.09 % higher accuracy retention than three popular baselines and 13.42 % with LLMRank compared to two popular baselines. Code is available at https://github.com/amazon-science/llm-rank-pruning.
@misc{hoffmann2024_llmrank, title = {LLM-Rank: A Graph Theoretical Approach to Pruning Large Language Models}, author = {Hoffmann, David B. and Budhathoki, Kailash and Kleindessner, Matthaeus}, year = {2024}, month = oct, day = {14}, eprint = {2410.13299}, archiveprefix = {arXiv}, primaryclass = {cs.LG}, url = {https://arxiv.org/abs/2410.13299}, }
2023
- arXiv
 Impact of HPO on AutoML Forecasting EnsemblesDavid B. HoffmannNov 2023
Impact of HPO on AutoML Forecasting EnsemblesDavid B. HoffmannNov 2023A forecasting ensemble consisting of a diverse range of estimators for both local and global univariate forecasting, in particular MQ-CNN,DeepAR, Prophet, NPTS, ARIMA and ETS, can be used to make forecasts for a variety of problems. This paper delves into the aspect of adding different hyperparameter optimization strategies to the deep learning models in such a setup (DeepAR and MQ-CNN), exploring the trade-off between added training cost and the increase in accuracy for different configurations. It shows that in such a setup, adding hyperparameter optimization can lead to performance improvements, with the final setup having a 9.9 % percent accuracy improvement with respect to the avg-wQL over the baseline ensemble without HPO, accompanied by a 65.8 % increase in end-to-end ensemble latency. This improvement is based on an empirical analysis of combining the ensemble pipeline with different tuning strategies, namely Bayesian Optimisation and Hyperband and different configurations of those strategies. In the final configuration, the proposed combination of ensemble learning and HPO outperforms the state of the art commercial AutoML forecasting solution, Amazon Forecast, with a 3.5 % lower error and 16.0 % lower end-to-end ensemble latency.
@misc{hoffmann2023_automl_forecasting, title = {Impact of HPO on AutoML Forecasting Ensembles}, author = {Hoffmann, David B.}, year = {2023}, month = nov, day = {7}, eprint = {2311.04034}, archiveprefix = {arXiv}, primaryclass = {cs.LG}, url = {https://arxiv.org/abs/2311.04034}, }